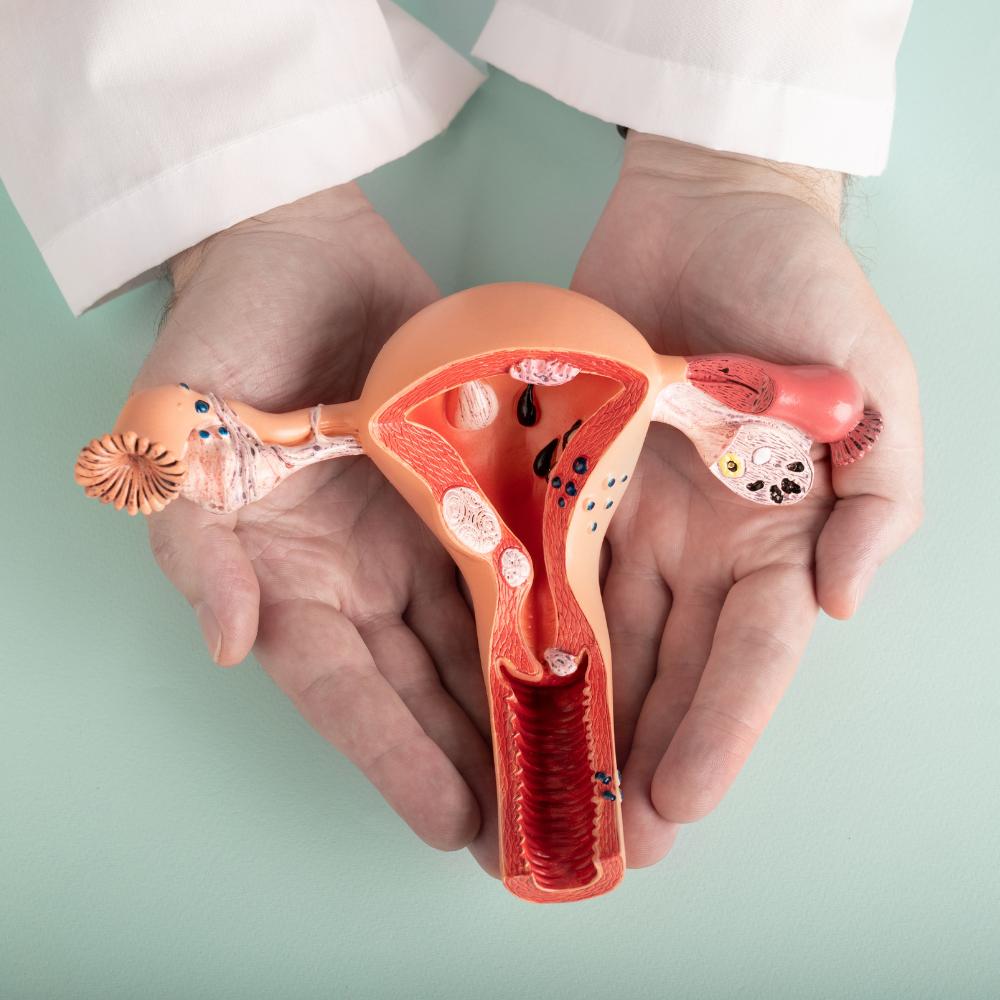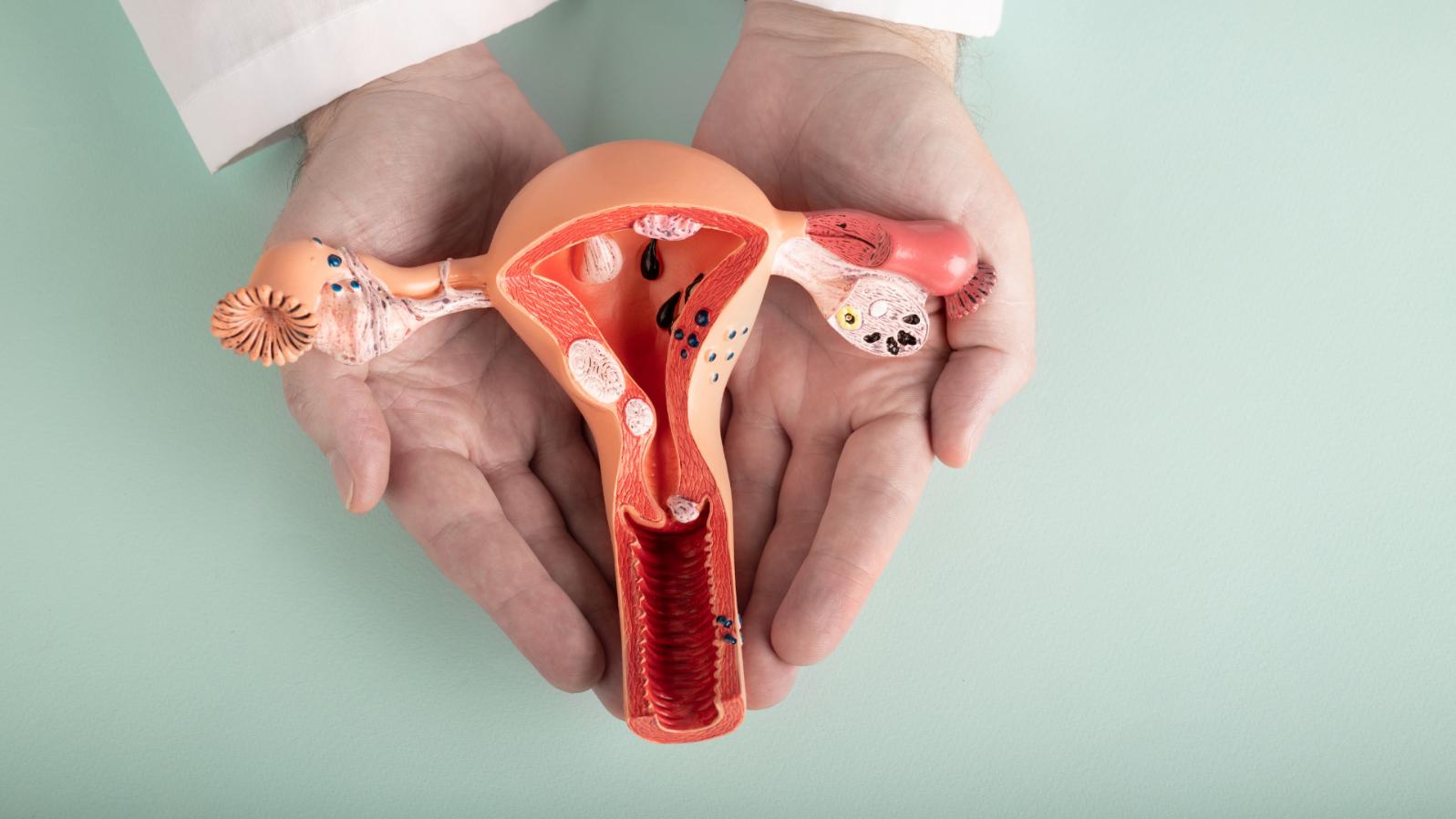
What is Hysteroscopy?
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that allows doctors to examine the inside of the uterus using a thin tube equipped with a camera, known as a hysteroscope. This procedure does not require any incisions; instead, a saline solution is used to expand the uterus for a clearer view.
Purpose of Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is primarily performed to identify and treat various abnormalities within the uterus, including:
– Heavy or irregular vaginal bleeding
– Submucosal fibroids
– Endometrial polyps
– Uterine scar tissue
– Retained or lost intrauterine devices (IUDs)
Preparation for Hysteroscopy
Preparing for a hysteroscopy involves several important steps:
– Preoperative Appointment: Schedule an appointment with your doctor to discuss the procedure.
– Health Assessment: Depending on your health, you may need to consult with specialists to ensure you are fit for surgery.
– Lab Work: Complete necessary lab work at least three days prior to the procedure.
– Medication Management: Discontinue certain medications as directed by your doctor.
– Smoking Cessation: It’s recommended to quit smoking 6-8 weeks before surgery to promote better recovery.
– Recovery Planning: Most women can expect a recovery period of 1-2 days.
Risks Associated with Hysteroscopy
While hysteroscopy is generally safe, there are potential risks, including:
– Bleeding
– Uterine perforation
– Damage to nearby organs (bladder, ureters, bowel)
– The need for conversion to laparoscopic or open surgery
– Rare risk of death
Post-Operative Risks
After hysteroscopy, you should monitor for signs of complications, such as:
– Blood clots
– Infection
– Scar tissue formation
Follow-Up Care
A follow-up appointment should be scheduled 4-6 weeks post-surgery to ensure proper recovery.
Hysteroscopic Myomectomy: Removing Fibroids
A hysteroscopic myomectomy is a specific type of hysteroscopy used to remove fibroids from the uterus.
Purpose
This procedure is performed when fibroids cause symptoms, and it’s important to note that only specific types of fibroids can be removed using this method.
Preparation and Risks
Preparation for a hysteroscopic myomectomy is similar to hysteroscopy. The risks also mirror those of hysteroscopy, including:
– Incomplete removal of the fibroid
– Uterine perforation
– Absorption of excess fluid
– Bleeding
– Damage to nearby organs
– Rare risk of death
Post-Operative Care
Follow-up care and potential risks after a hysteroscopic myomectomy are the same as for hysteroscopy.
Hysteroscopic Polypectomy: Removing Polyps
Hysteroscopic polypectomy is another minimally invasive procedure aimed at removing uterine polyps.
Purpose
This procedure is utilized for removing polyps inside the uterus that may be causing symptoms.
Preparation and Risks
Preparation and associated risks are similar to those of a hysteroscopic myomectomy.
Post-Operative Care
As with other procedures, a follow-up appointment should be scheduled 4-6 weeks after surgery.
Laparoscopy: A Broader Scope
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique that involves making small incisions in the abdomen to diagnose or treat various pelvic conditions.
Purpose
Laparoscopy is commonly used to treat conditions like endometriosis, ovarian cysts, and adhesions.
Preparation for Laparoscopy
Similar to other procedures, preparation includes:
– Preoperative appointment
– Required lab work
– Specific instructions regarding bowel preparation and medication management
Risks
Risks associated with laparoscopy include:
– Bleeding
– Infection
– Damage to surrounding organs
– Conversion to open surgery
– Rare risk of death
Post-Operative Risks
Potential post-operative risks include urinary retention, blood clots, bowel obstruction, and recurrence of symptoms.
Follow-Up Care
A follow-up appointment is typically scheduled two weeks after the procedure.
Hysteroscopy and Endometrial Ablation
Combining hysteroscopy with endometrial ablation, this procedure aims to treat heavy vaginal bleeding by burning the lining of the uterus.
Purpose
Endometrial ablation is used specifically for managing heavy menstrual bleeding.
Preparation, Risks, and Follow-Up
Preparation and risks are similar to hysteroscopy, with the addition of potential post-operative concerns such as persistent pelvic pain and scar tissue formation. A follow-up appointment should be scheduled 4-6 weeks after surgery.
Conclusion
Understanding these procedures can help women take charge of their health. If you have any questions or concerns regarding hysteroscopy or any related procedures, consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. Being well-informed is the first step toward a healthier future.